雖然現在可以透過 Deep neural networks 來訓練出非常強大的能力,但卻難以學到比較通用的知識,通常最後訓練出的 model 會只適合處理類似於 training data 的資料。
Domain adaption 是目前在 machine learning 比較新的問題,是希望可以讓 network 學到比較跨領域的 features ,進而使訓練出來的模型可以應用在不同 domain 的資料上。
這篇論文[1] (Deep CORAL: Correlation Alignment for Deep Domain Adaptation, B Sun, K Saenko, ECCV 2016) 提出一個 CORAL loss,通過對 source domain 和 target domain 進行線性變換來將他們各自的的二階統計量對齊 (minimizing the difference between source/target correlations).
Introduction
- 作者引入了 CORAL[2] 這一方法,並且將其擴展成一 differentiable loss function。
- 作者藉由 CORAL loss 來做 unsupervised learning,並達到了 state-of-the-art 的 performance。
- CORAL loss 十分簡單並且可以輕易地整合至一般的神經網路中。
Architecture
![作者將 CORAL loss 加進一分類問題的網路架構中。 <sup>[1]</sup>](/img/2017-10-31/1.png) 作者將 CORAL loss 加進一分類問題的網路架構中。 [1]
作者將 CORAL loss 加進一分類問題的網路架構中。 [1]作者將 Deep CORAL 應用在一般的分類問題上,整個神經網路架構如圖。從中間 cov1 ~ fc8 其實就是一般的 AlexNet,只是稍作修改改成有兩個 input (source data & target data) 以及兩個 output。
在訓練的過程中,每個 batch 都包含了 source data & target data,其中 source data 是包含 label 資料的;而 target data 則完全沒有 label 資料。
source data & target data 各自經過一 shared weight 的 networks 之後會有兩個 output,其中:
- source task 會算一個 classification loss
- source 的
fc8及 target 的fc8會再拿來算 CORAL loss
而總和 loss 為兩者相加:
CORAL Loss
作者提出的 CORAL loss 是在計算 source & target covariance matrix 之間的 distance。
We define the CORAL loss as the distance between the second-order statistics
(covariances) of the source and target features.
Forward
而這個 loss function 定義如下:
其中,
詳細符號定義可以參考 paper[1] section 3.1
Backward (gradient)
至於 gradient 可以由 chain rule 算出來,如下:
注意 target 那邊是有個負號的,當初在實作時忘記這個負號而搞半天…
Experiment
作者做的實驗也是在分類問題上,架構如同上面提及的神經網路架構圖。
實驗採用 Office31 dataset[3],這是一個專門拿來做 domain adaption 的資料集,裡面有三種不同 domain 的影像: Amazon, DSLR, and Webcam
裡面都有相同的 31 種類別,也就是說這三大類唯一不同的點就是圖片的樣貌:
- Amazon 就是去背的圖片(背景都是白色的)
- DSLR 就是用單眼拍的圖片(背景就是真實場景的背景)
- Webcam 跟 DSLR 很相近,差別比較大的部分是 webcam 的畫質比較差,有的還有色偏
在實驗進行過程中,source data 會有 label;而 target data 則沒有。
且在開始之前會先預載 ImageNet pre-trained model。
由於 Office31 有三種 domain data,所以作者就做了所有 domain adaption 的組合,以下是結果圖:
![各種方法比較圖。螢光的是作者的方法。<sup>[1]</sup>](/img/2017-10-31/2.png) 各種方法比較圖。螢光的是作者的方法。[1]
各種方法比較圖。螢光的是作者的方法。[1]可以看到 D-CORAL 在大部分的 domain adaption tasks 中都取得了最好的成績。
再來看看其中一個實驗 Amazon → Webcam 的詳細結果:
![Amazon → Webcam 的詳細結果圖。<sup>[1]</sup>](/img/2017-10-31/3.png) Amazon → Webcam 的詳細結果圖。[1]
Amazon → Webcam 的詳細結果圖。[1]圖 (a) 比較了有 CORAL loss 與沒有 CORAL loss 的差別,可以看到當加入CORAL loss 之後,target (test) task 有顯著的提升,而且並未使得 source (training) task 的準確率下降太多。
圖 (b) 則可以看出,classification loss 跟 CORAL loss 其實是扮演互相抗衡的腳色,隨著訓練的進行會讓兩者到達一穩定的狀態。
Implementation
我也試著用 PyTorch 實做了此篇論文的方法,最重要的其實就是新增一 loss function 到整個網路架構中,其中 forward and backward 的算法剛好也有詳細說明。
Forward 的部分大概如下:
1 | def forward(self, source, target): |
Backward 則如下:
1 | def backward(self, grad_output): |
寫起來公式的部分又臭又長 XD
我也實際跑了 Amazon → Webcam 的例子,做了個圖:
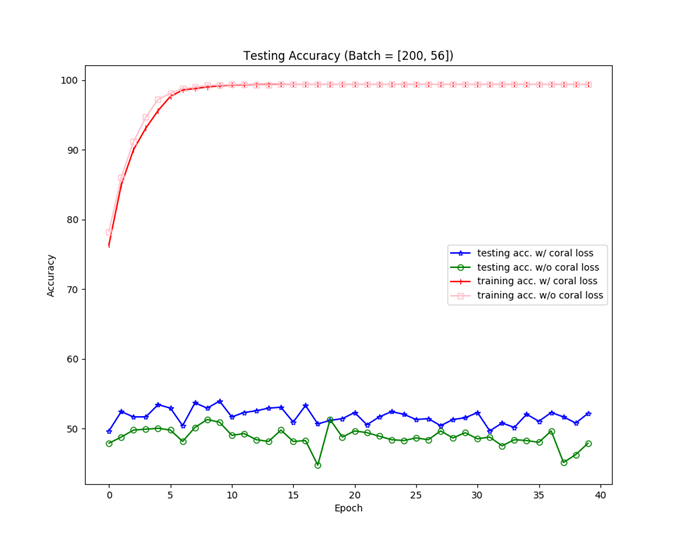 我做出來的 Amazon → Webcam 的詳細結果圖。
我做出來的 Amazon → Webcam 的詳細結果圖。可以看出有 CORAL loss 的確使得 target task 的準確率提升一些。
不過我做出來的整體準確率並沒有與論文上的一樣有 60% 左右,而是大概在 50% 左右,不知道為甚麼… QQ
Update
經過 redhat12345 的建議後,修正了一下 CORAL Loss 的算法,終於使 Target accuracy 提升到原論文的程度。
1 | def CORAL(source, target): |
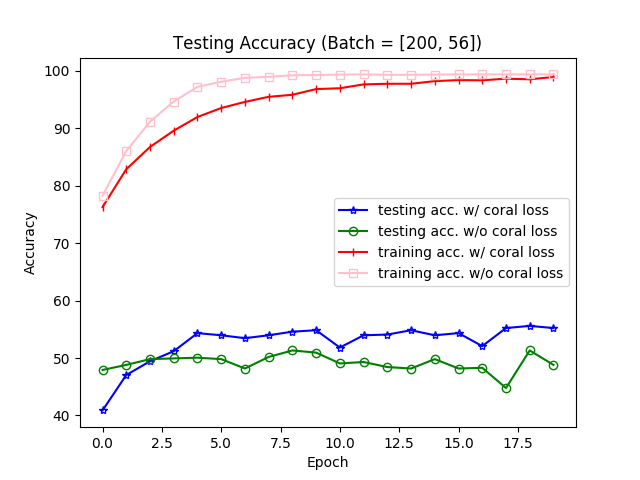 修正過後的結果。
修正過後的結果。References
- Sun, B., Saenko, K.: Deep CORAL: Correlation Alignment for Deep Domain Adaptation. In: ECCV (2016)
- Sun, B., Feng, J., Saenko, K.: Return of frustratingly easy domain adaptation. In: AAAI (2016)
- Domain Adaptation Project